


Flat bottom steel silo play an important role in modern grain storage. They are not only popular among large farms for their large storage capacity, but also have a very intelligent detection system and a stable and safe grain security system. So should we choose flat-bottomed steel silos for normal storage? In fact, this is wrong. We must choose the type of silo based on the specific working conditions, material characteristics and economic efficiency. Today, we will explain the decision-making scenarios and selection logic for choosing flat bottom steel silo.
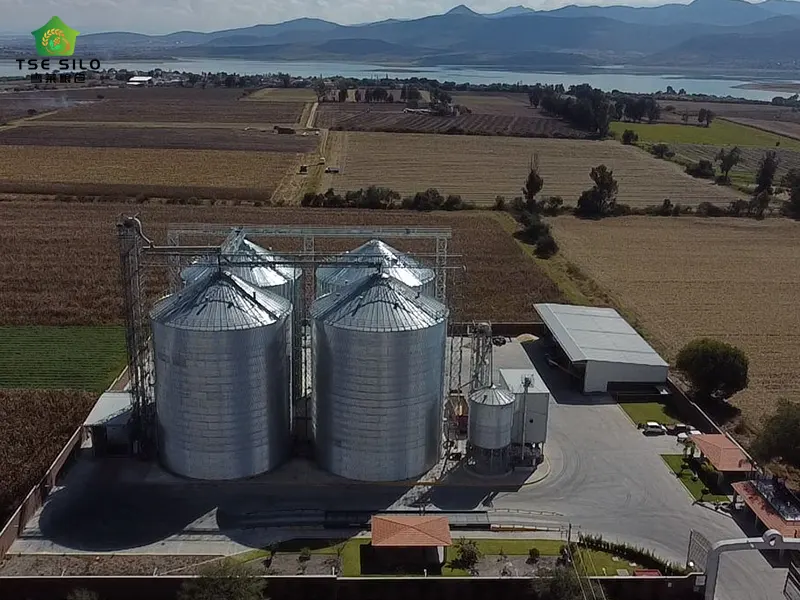


Overview: This is mainly used in large farms for grain storage. Flat-bottomed steel silos can store grain safely and for a long time with their good monitoring system.
Advantages: The flat-bottomed structure has no cone bucket dead corners, and the space utilization rate is >95% (only 80%~85% for cone-bottomed silos).
Case: A 100,000-ton grain storage project can save 30% of land by using a flat-bottomed silo.
Overview: Materials with poor fluidity are what we usually refer to as stagnant materials with large inventory, very little consumption, and very low inventory turnover.
Applicable materials:
Fly ash, cement (easy to compact)
Wet grain (moisture content >18%)
Sludge, clay
Solution: Flat-bottomed silo + fluidizing rod/sweeper (residual rate < 0.5%).
Overview: Limited site means storing more materials in a limited area. Here it is mainly compared with the cone-bottom steel silo. The bearing capacity of the bottom of the cone-bottom steel silo is limited, generally around 1,000 tons.
Cost comparison:
| Project | Flat-bottom silo | Cone-bottom silo |
| Steel usage | Save 20%~30% | Cone bucket additional consumables |
| Foundation cost | Reduce 15% | Deep foundation required |
Flat-bottom silos can be connected side by side horizontally to form a continuous silo group (such as a grain enterprise silo matrix).
Flat-bottom silos have a low center of gravity, and can reduce seismic response by 40% with sliding bearings (in line with GB 50011 specifications).
Flat-bottom silo tops can be installed with:
Photovoltaic panels (for self-use)
Dust removal system (cement/chemical silo)
Intelligent monitoring sensors
Quick installation (bolted silos built in 3 days), suitable for temporary storage.
Cone-bottom silos rely on inclination (>55°) to achieve zero-power unloading, and flat-bottom silos require additional energy to drive unloading equipment.
Cone-bottom silos have lower overall costs (simplified unloading system).
Cone-bottom silos have no unloading dead corners, making it easier to achieve full silo anti-corrosion coating coverage (such as chemical acid slag storage).
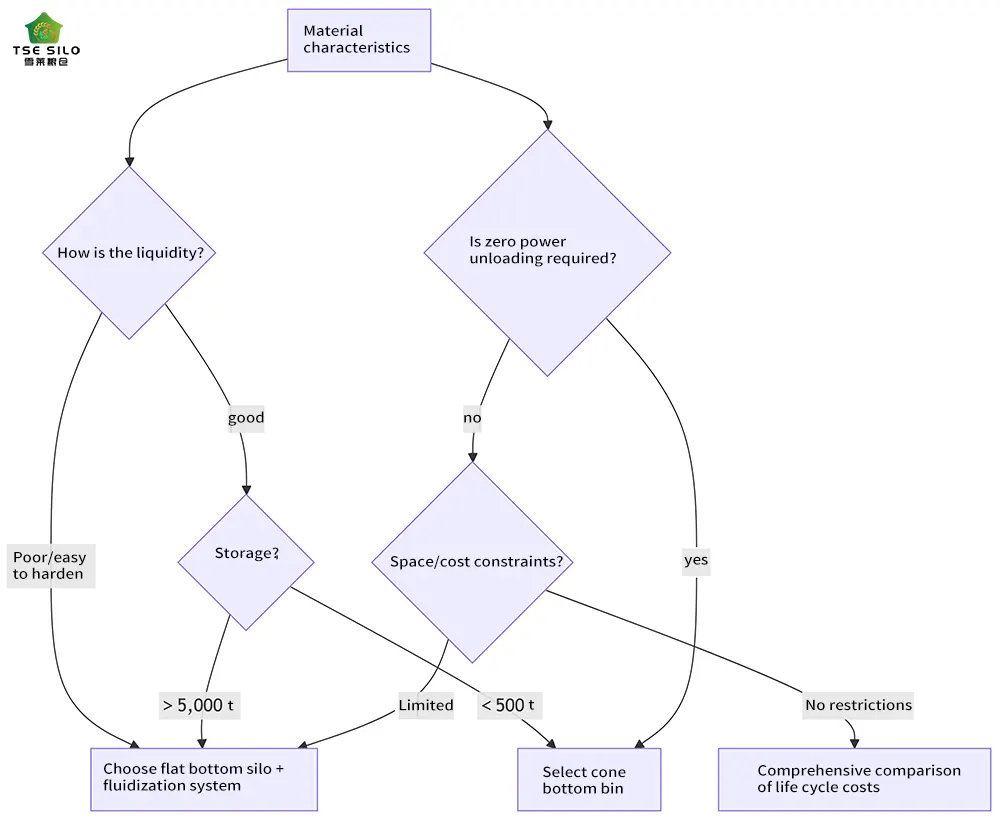
If you choose a flat-bottom silo, you must optimize the following systems:
Fluidizing rod: air pressure 0.2~0.5MPa, layout density ≥1 bar/4㎡
Sweeper: rotary scraper power ≥7.5kW (residual rate < 0.3%)
Slope of silo bottom ≥1° (tilted toward the discharge port)
Inner wall polishing (Ra≤0.8μm)
Material level radar (error ±0.5%)
Humidity sensor (anti-condensation warning)
Total cost of flat-bottom silo = silo construction cost × 1.3 (unloading system) + energy consumption × annual operating hours.
When it meets: Total cost of flat-bottom silo < Total cost of cone-bottom silo × 1.1, the flat bottom steel silo is better.
Note: 1.3 is the unloading system coefficient; 1.1 is the cone bottom silo foundation increment coefficient.
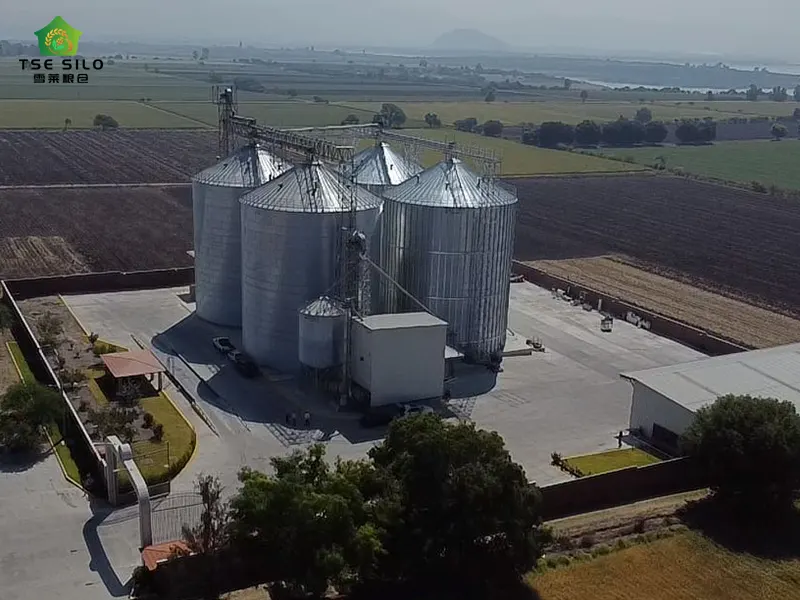


European standard: EN 1993-4-1 (Steel silo structure design)
American standard: ACI 313 (Concrete and steel silo specification) + ASCE 7 (Load calculation)
Chinese national standard:
GB 50322 "Grain Steel Silo Design Specification"
GB 50077 "Reinforced Concrete Silo Design Specification" (Steel Silo Reference)
| Parameters | Calculation logic | Example value |
| Wall thickness | Based on material side pressure + wind load/seismic force | 3~20mm (Q345 steel) |
| Circumferential stiffening rib spacing | Prevent buckling instability (L≤1.5m) | 0.8~1.2m |
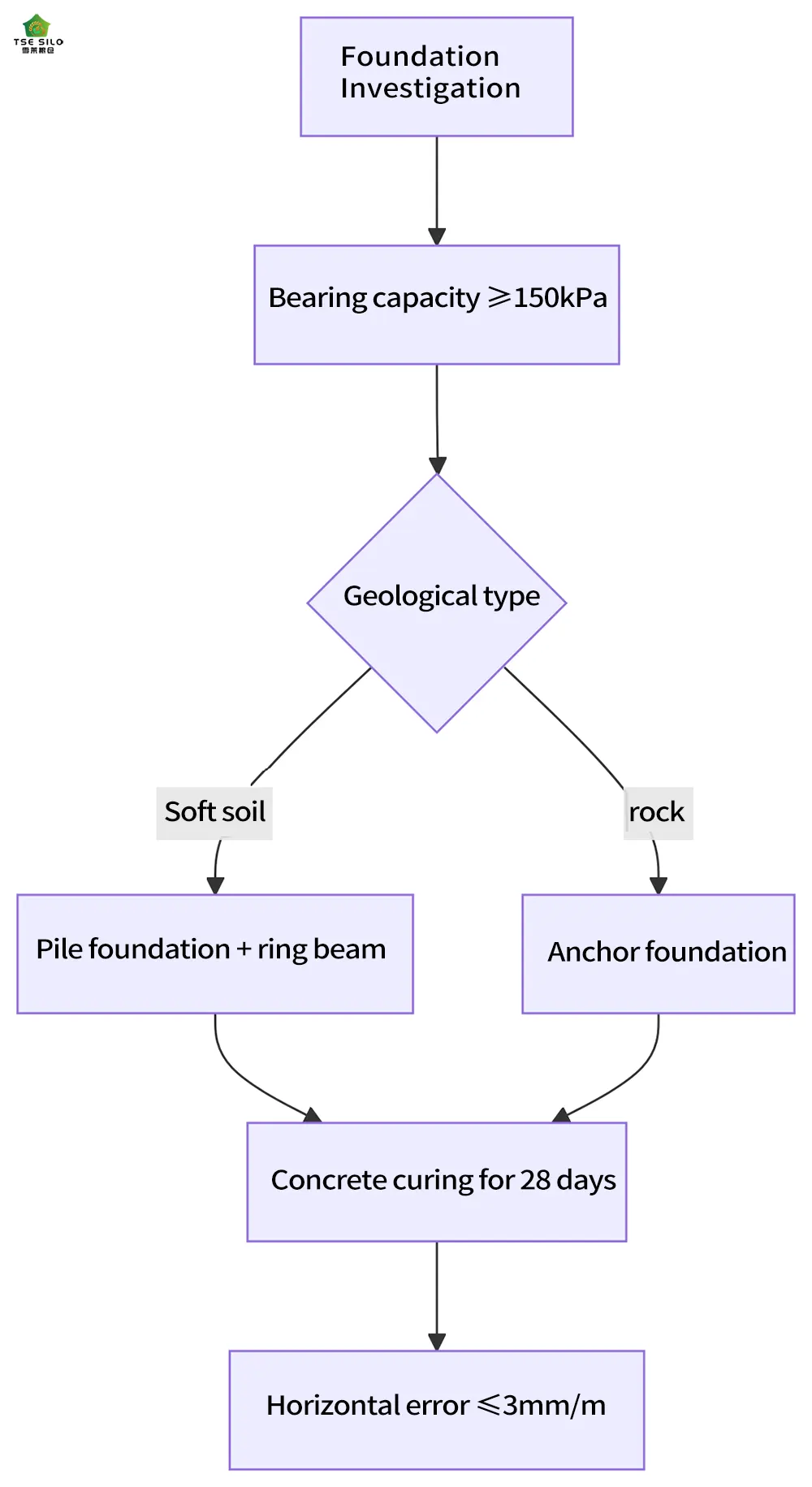
| Foundation load | Full warehouse deadweight + dynamic load (1.5 times safety factor) | 200~500 kN/m² |
| Stage | Technical points | Detection tools |
| Bottom plate welding | Continuous full welding (penetrant flaw detection) | Ultrasonic flaw detector |
| Wall plate coiling | Bottom-up spiral bite (overlap ≥40mm) | Laser verticality meter |
| Top cover hoisting | Air pressure lifting method (synchronization error ≤5mm) | Strain sensor |
For the selection of steel plate silo type, we must consider the silo capacity, liquidity, storage and construction cost. In terms of steel plate silo construction, Shandong Xuelai Grain Storage Co., Ltd. has many years of experience in steel plate silo construction. The company's technical team can provide you with a detailed steel plate silo construction plan based on your needs and storage site survey. Shelley Steel Silo fully complies with all international standards for the construction of flat-bottom steel silos. The company has classic cases in major grain-producing countries such as Canada and Mexico. Customers who need to build steel silos are welcome to call Shelley for consultation.
Written by
Shandong Shelley Grain Steel Silo Co., Ltd
Editor Jin
www.grainstoragesilos.com
WhatsApp : +86-18653877118
Email : shelley@cnshelley.com